The technique of delivering computing services over the internet is known as cloud computing. Cloud infrastructure is a virtual platform that supports cloud computing, which employs virtual resources to give us a seamless application experience. We can say “infrastructure” refers to the all hardware, that is used in data centers. So we can consider cloud infrastructure as the equipment required to create a cloud.
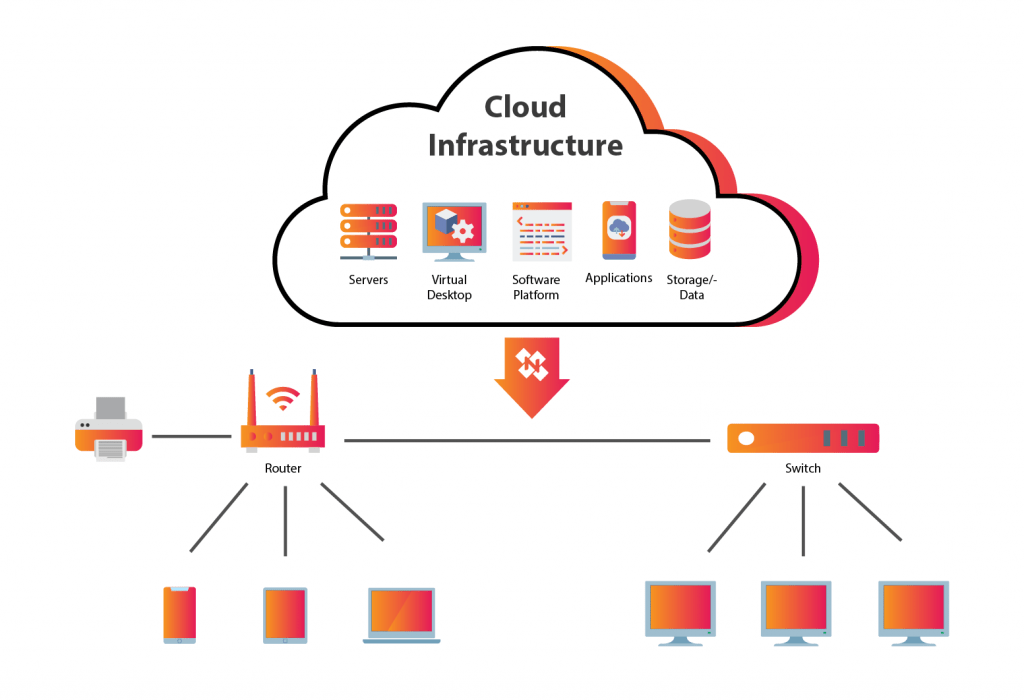
Thanks to the cloud architecture, businesses can get computing and data storage requirements whenever they need them. Instead of building on-premises IT systems or renting data center space, organizations can lease cloud infrastructure and required computing resources from third-party cloud service providers.
Components of Cloud Infrastructure
The cloud’s architecture is extensive and complicated. With the exception of being virtualized and used over the Internet, it is identical to standard data center architecture.
There are four main components of cloud infrastructure:
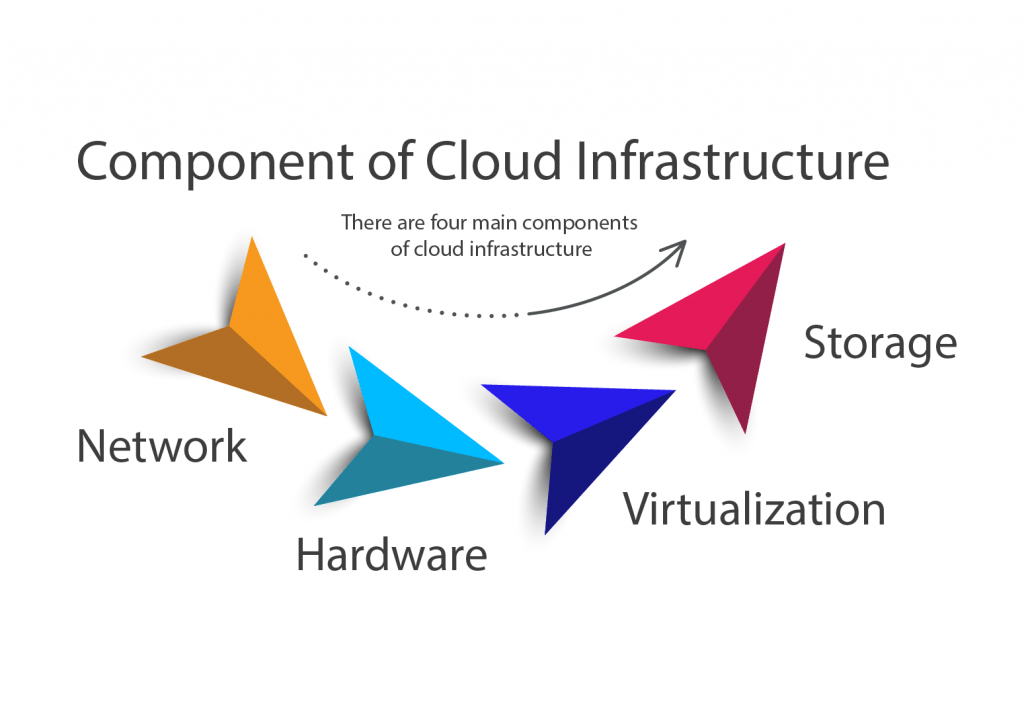
Network
Physical network components like routers, switches, and wires constitute the foundation of cloud networks, with additional virtual networking hardware placed on top. Multiple subnetworks comprise them, and those subnetworks are subsequently utilized to build virtual local area networks (VLANs).
Hardware
There is a lot of complex hardware in the cloud service provider’s data centers.
A cloud network is composed of a range of physical components that may be dispersed over several different places. The hardware consists of servers, storage arrays, backup equipment, switches, routers, firewalls, and load balancers for networking. The servers are linked using virtualization, which divides and abstracts resources to make them available to consumers.
Virtualization
Running a computer system as a virtual instance in a layer separate from the actual hardware is called virtualization. It most frequently refers to using many operating systems at once on a computer system. The operating system, libraries, and other programs that make up the guest system are distinct from the host operating system that runs below it, giving the impression the software operating on the virtualized system that they are on a separate computer.
The resources of the system, including memory, processing power, and storage, are abstracted by a software called a hypervisor, which is installed on top of the machine’s physical hardware. This is also called Hardware virtualization. In order to construct an abstraction layer on computer hardware, virtualization requires software. This layer enables the division of a single computer’s physical components—such as its CPU, memory, and storage—into several virtual computers, also known as virtual machines (VMs). A virtual computer provides a setting that is logically isolated from the physical machine.
Storage
Data storage and access over the internet are made possible by cloud storage. Organizational data may be used and stored almost anywhere with the use of cloud infrastructure. Storage space is decoupled from hardware systems through virtualization so that users can access it as cloud storage.
Basic Requirements for Effective Cloud Infrastructure Management
All the settings made on the cloud computing infrastructure are known as cloud infrastructure management. Providing highly scalable and integrated computing units, hardware and software, to maintain the security of all types of data belonging to many different clients is the primary objective of cloud infrastructure management. Utilizing the same infrastructure like this, reduces running costs over time.
To maintain a reliable infrastructure, various detailed measures must be done while developing a cloud plan:
Service Management
Using a public and/or private cloud vendor, end users can quickly deploy and administer a measured package of applications and services known as service management. Administrators need the appropriate instruments for the description of the services in order to commercialize cloud capability. A service package should contain, as a minimum, all information regarding pricing guarantees, implementation and billing. Once implemented, management services should assist in developing data and workflow policies to guarantee that data is fully functional and that processes are sent to cloud-based systems.
Reliability, Availability, and Security
Cloud computing has changed the paradigm and architecture of how IT services are provided and used. However, it is still important that these new solutions contain the same components required for end users. Users want the cloud to be available at all times and the cloud must be able to keep running while the data is still intact in the virtual data center in order to be completely reliable and available. Cloud infrastructures must continue to function even if one or more components fail for them to be completely reliable.
One of the most crucial concerns that cloud providers focus on is cloud security. Services must guarantee that data and apps are secure while granting access to those who are allowed in order to protect the cloud. As long as businesses keep records and store sensitive data, cyber threats including data loss and leakage, malware/ransomware attacks, phishing, and denial of service attacks will exist. Those threads will be the same whether your data is on-premise or on the cloud. Enforcing isolation and maintaining a secure virtualized infrastructure are the main security requirements of the cloud provider.
Data Center Management Tools
Despite the fact that the cloud is a novel method to consume IT, many aspects of traditional data center governance require a certain level of integration. Many different cloud management tools are used in most data centers for provisioning, customer service, billing, systems administration, directory, security, and much more. These instruments are not replaced by cloud infrastructure management solutions. Cloud services should take advantage of cutting-edge software, hardware, virtualization, and other technologies while supporting a data center’s current architecture.
Users, Admins, and Developers Interfaces
To create a genuinely successful cloud, however, businesses and service providers need to be aware of the components that it must have. Self-service interfaces and distribution strategies aid in protecting the end user from the cloud’s complexity. Considering that the end-user handles the majority of management duties, this promotes adoption and lowers operational expenses. The user is able to develop and launch templates as well as administer his or her own virtual data center and virtual storage. The user can control network and computing resources as well as access picture collections.
User interface for administrators should allow single point access to all cloud computing services. They should be able to see real resources, virtual machine instances, service offerings, templates, and users. All of these functionalities should be accessible to developers via standard APIs.
Reporting and Visibility
To ensure service level agreements, compliance, billing, and security in cloud settings, data centers require high levels of real-time reporting and visibility capabilities. Managing all those activities is very difficult without reliable information and visibility. Cloud infrastructures must continue to function even if one or more components fail for them to be completely reliable. Services must guarantee that data and apps are secure while granting access to those who are allowed in order to protect the cloud.
What is the Key Component of Cloud Infrastructure Management?
On-premises data centers are difficult to maintain and have become places that impose significant financial burdens for many businesses. As a result of greater scalability, reliability, cost savings, and security, application delivery chains increasingly stretch well beyond a company’s four walls and into the cloud. Monitoring of the infrastructure is a crucial part of achieving ideal cloud infrastructure management.
IT professionals may more effectively and efficiently address the root cause of performance issues thanks to the automation of information gathering and assessment by IT infrastructure monitoring technologies. A proactive examination of the application architecture guarantees that network resources are being used as intended and enables you to anticipate or uncover performance issues before they become urgent.
Performance monitoring tools that help with infrastructure management are essential to lowering outages and boosting reaction times due to the complexity of the current IT infrastructure. A steady stream of alerts might easily turn into an irrelevant flood of data due to the density of infrastructure components.
The ability to prioritize issues based on user-defined criteria and/or artificial intelligence frees up DevOps‘ time and focus so they can solve crucial issues that could cause outages or downtime. solitary system surveillance The static, self-contained nature of technology stacks has changed. Monitoring servers and databases on-premises, in the cloud, or in a hybrid environment, is the task of monitoring services to manage all cloud computing infrastructure and quickly troubleshoot the problems.
Cloud infrastructure management challenges
While migrating to the Cloud is essential for keeping your company current, you can’t simply adopt it and walk away. To make sure you’re not overlooking anything, it takes ongoing management. Cloud infrastructure management challenges come with various challenges.
According to Flexera 2022 State of the Cloud Report the top three challenges are security, lack of resources/expertise, and managing cloud spending. Security was the number one challenge facing respondents in ten of the eleven State of the Cloud reports.
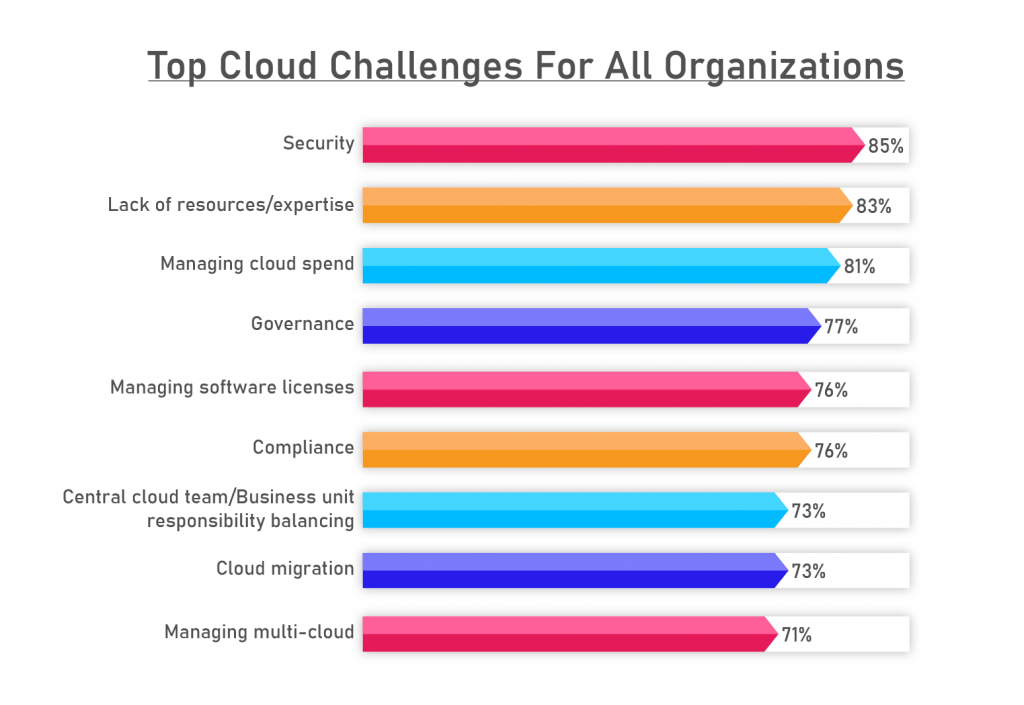
Below are a few of the most significant ones:
Security
Cloud security is the top challenge for both enterprises and small businesses. The main cloud security challenges are :
- Data Loss and Leakage
- Unauthorized Access
- Malware/Ransomware Attacks
- Phishing Attacks
- Denial of Service Attacks
Security and compliance are shared responsibilities between the cloud provider and the customer.
For fulfilling the customer responsibilities cloud consulting services may be the best option for you to make your cloud secure.
Lack of Resources/Expertise
Finding expertise in cloud computing is becoming a bottleneck for many organizations as the use of cloud technologies grows, the tools to manage them become more advanced, and the tools themselves become more complex. Although many businesses are embracing automated cloud management technology, it is always preferable to train people to meet the demand for time. Besides cloud providers’ own tools the IT sector makes extensive use of DevOps tools like Terraform, Ansible, Chef and Puppet.
Managing Cloud Spent
If you don’t implement effective management methods, cloud computing can be pricey. Many times, businesses adopt a pay-as-you-go mentality and invest more in cloud services than they would have in on-premise infrastructure. For improved cost monitoring, cost optimization should always be done through financial analytics and utilization reporting.
Governance
Although effective cloud governance is crucial, many businesses lack a well-thought-out cloud strategy. Security issues are made more likely by all the advantages of the Cloud, including its flexibility, reduced cost, and speed. For businesses that switch to this paradigm, the Cloud’s decreased barrier to service consumption presents a serious challenge. There are many difficulties, such as those related to access, cost, and data protection. A few solutions from cloud providers can help you manage governance more efficiently, but more is required to maintain a firm grip on compliance and cloud security.
What are the best practices of Cloud Cloud Infrastructure Management?
Managing cloud infrastructure is essential to get the best from cloud computing. When managed and optimized properly, the cloud gives businesses more flexibility and scalability for their infrastructure and applications while lowering expenses. Organizations and end users reduce the costs associated with purchasing and maintaining the physical infrastructure these virtual resources mirror by consuming virtual resources via the cloud and even paying for these resources on an as-needed basis.
Security and compliance:
Safeguard your cloud-based systems and information assets.
Reliability and resilience:
Create resilient cloud infrastructure to support the development of dependable apps.
Optimizing performance and costs:
Make optimal use of infrastructure resources to achieve the highest performance at the lowest cost.
Operational effectiveness:
Manage your infrastructure resources, applications, and operations to provide the greatest possible business value.
Difference between Private, Public, and Hybrid Cloud Architectures
Cloud infrastructure is offered for private, public, and hybrid cloud systems. It can also be hired from cloud service providers and through a variety of cloud infrastructure delivery mechanisms. The three cloud computing models all leverage the same fundamental elements of cloud infrastructure to provide computing services.
Public cloud
A public cloud architecture uses outside cloud service providers to make cloud resources accessible to many users online. These service providers run multi-tenant settings that lower the price of computer power and data storage for clients. Customers can save money as a result. Additionally, it ensures increased productivity by streamlining procedures and enabling user cooperation.
The overall cost of computing resources can be decreased by using this strategy, however, for firms handling sensitive data or personally identifiable information, it may offer privacy concerns.
Private Cloud
Only one business can access cloud infrastructure in a private cloud architecture approach. The private cloud architecture may be created, developed, and managed by an organization’s internal IT staff or by third parties.
Hybrid Cloud
Companies often build their cloud strategies on hybrid cloud. General data security, cost advantage and data integration are among the reasons why hybrid cloud is preferred. With this strategy, businesses that deal with PII and sensitive data can keep their most important data in private clouds and less important data in public clouds.
The hybrid cloud has the benefits of both public and private environments. The hybrid solution can limit the amount and type of data in the public cloud. Thus, security risks can be reduced. The hybrid cloud also allows businesses to increase operational efficiency by combining public and private processes.
How Can Cloud Technology Benefit Your Business?
Even before the introduction of cloud computing, the flaws of traditional IT infrastructure have been clear, and this trend is still going strong. Due to the inability of their technology environments to detect and respond to these changes in the marketplace and new trends, many businesses today struggle to adapt. Today’s competitive environment forces companies to minimize complexity, reduce costs and accelerate the delivery of technology services while maintaining control over IT.
Changing to cloud might lower the operation and maintenance costs of your IT infrastructure. Instead of purchasing expensive systems and equipment for your business, you may save money by using the services provided by your cloud providers.
Data and system security is a crucial component of business continuity planning. When your data is stored in the cloud, it is protected against disasters, power cuts, and other catastrophes by being backed up and stored in a safest way.
If you were considering implementing cloud computing as well check NioyaTech’s Cloud Solutions Services.